getDesignGroupSequential()
getDesignInverseNormal()
getDesignFisher()
getDesignConditionalDunnett()Designing Clinical Trials in R with rpact and crmPack
Introduction for Roche Biostatistics
RPACT
January 13, 2026
Executive summary 📝
- RPACT has been collaborating closely with Roche since RPACT inception in 2017
- We present two RPACT open source R packages for clinical trial design:
- For both R packages, Roche has a Service Level Agreement (SLA) with RPACT for professional support, training, validation and development
- In total, 21 companies are currently having SLA with RPACT (21 for
rpact, 4 forcrmPack)
- In total, 21 companies are currently having SLA with RPACT (21 for
- In addition, we present briefly RPACT Cloud, a new web-based GUI for
rpact, which is currently licensed by 4 pharmaceutical companies
Ecosystem in R 🌏
- From: First R package for clinical trial design was likely
S+SeqTrial- Developed for S-PLUS by Emerson (2000)
- Available for free at rct-design.com
- To: Clinical Trials CRAN task view
- As with other areas of R packages, the quality varies
- Professional support, testing and documentation are crucial for long term stability and value
- Comparison with Posit (formerly RStudio) supporting important general purpose packages like
shiny,tidyverse,dplyr,ggplot2
The RPACT User Group
- AbbVie
- Allucent
- Bayer
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Dr. Falk Pharma
- Dr. Willmar Schwabe
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche
- FGK Clinical Research
- Gilead
- GKM
- Johnson & Johnson
- Merck
- Metronomia Clinical Research
- Nestlé
- Novartis
- Parexel
- Pfizer
- PPD (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Recursion
- Sanofi
- UCB
rpact
Overview 📦
- Comprehensive validated R package implementing methodology described in Wassmer and Brannath (2025)
- Enables the design of traditional and confirmatory adaptive group sequential designs
- Provides interim data analysis including early efficacy stopping and futility analyses
- Enables sample-size reassessment with different strategies
- Enables treatment arm selection in multi-stage multi-arm (MAMS) designs
- Enables subset selection in population enrichment designs
- Provides a comprehensive and reliable sample size calculator

Developed by RPACT 🏢
- RPACT company founded in 2017 by Gernot Wassmer and Friedrich Pahlke
- Idea: open source development with help of “crowd funding”
- Currently supported by 21 companies
- \(>\) 80 presentations and training courses since 2018, e.g., FDA in March 2022
- 30 vignettes based on Quarto and published on rpact.org/vignettes
- 32 releases on CRAN since 2018
- October 2025: Daniel Sabanés Bové joined RPACT as partner



Trial Designs 🔬
- Fixed sample designs:
- continuous, binary, count, survival outcomes
- Group sequential designs:
- efficacy interim analyses, futility stopping, alpha-spending functions
- Adaptive designs:
- Inverse normal and Fisher’s combination test, conditional error rate principle
- Provides adjusted confidence intervals and bias corrected estimates
- Multi-arm multi-stage (MAMS) and enrichment designs, sample size reassessment
Easy to understand R commands:
Sample Size and Power Calculation 💻
Sample size and power can be calulcated for testing:
- means (continuous endpoint)
- proportions (binary endpoint)
- hazards (survival endpoint)
- Note: flexible recruitment and survival time options
- rates (count endpoint)
Example: Sample Size Calculation 🧮
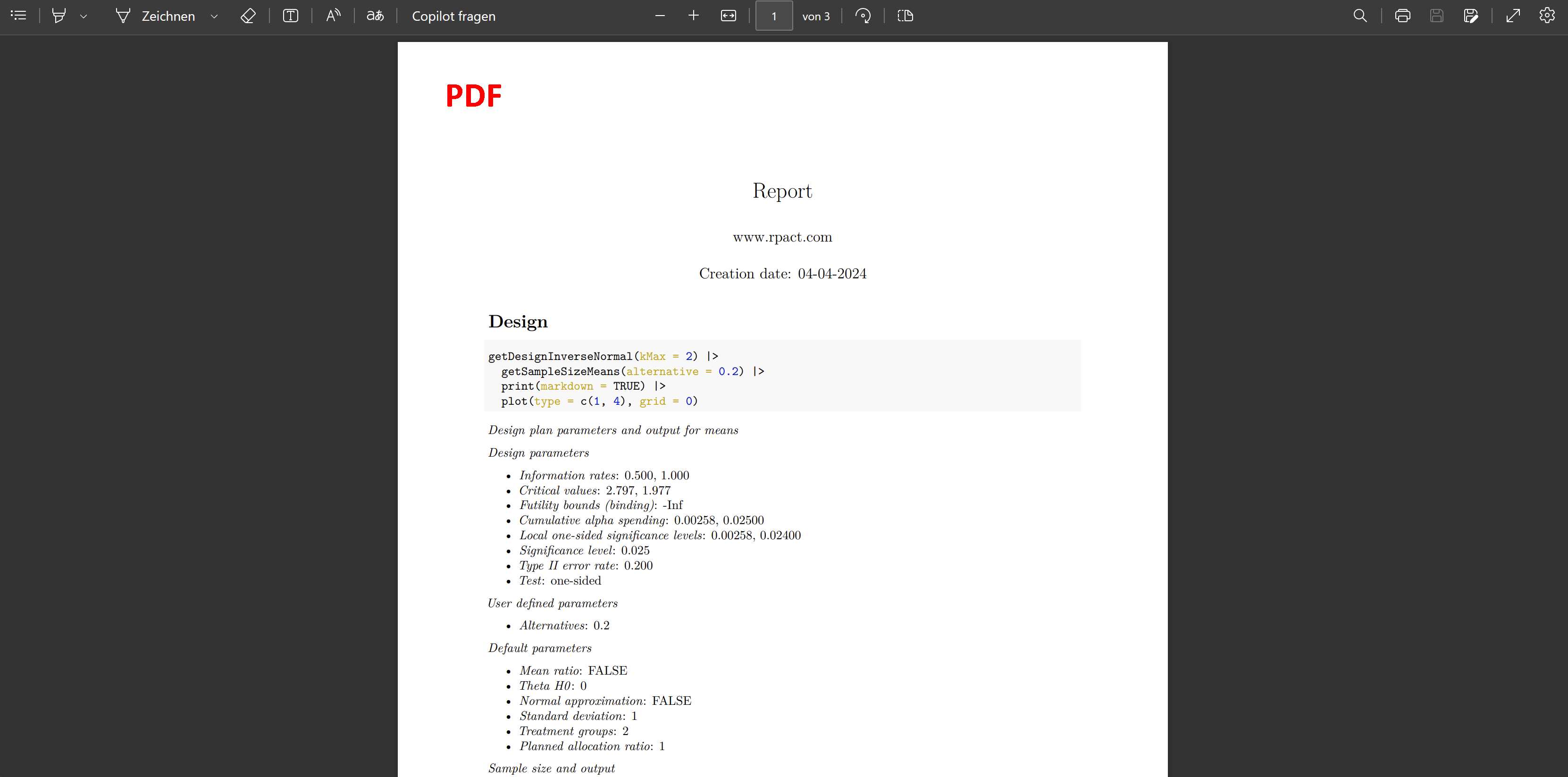
Sample size calculation for a continuous endpoint
Sequential analysis with a maximum of 3 looks (group sequential design), one-sided overall significance level 2.5%, power 80%. The results were calculated for a two-sample t-test, H0: mu(1) - mu(2) = 0, H1: effect = 2, standard deviation = 5.
| Stage | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planned information rate | 33.3% | 66.7% | 100% |
| Cumulative alpha spent | 0.0001 | 0.0060 | 0.0250 |
| Stage levels (one-sided) | 0.0001 | 0.0060 | 0.0231 |
| Efficacy boundary (z-value scale) | 3.710 | 2.511 | 1.993 |
| Futility boundary (z-value scale) | 0 | 0 | |
| Efficacy boundary (t) | 4.690 | 2.152 | 1.384 |
| Futility boundary (t) | 0 | 0 | |
| Cumulative power | 0.0204 | 0.4371 | 0.8000 |
| Number of subjects | 69.9 | 139.9 | 209.8 |
| Expected number of subjects under H1 | 170.9 | ||
| Overall exit probability (under H0) | 0.5001 | 0.1309 | |
| Overall exit probability (under H1) | 0.0684 | 0.4202 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H0) | 0.0001 | 0.0059 | |
| Exit probability for efficacy (under H1) | 0.0204 | 0.4167 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H0) | 0.5000 | 0.1250 | |
| Exit probability for futility (under H1) | 0.0480 | 0.0035 |
Legend:
- (t): treatment effect scale
Adaptive Analysis 📈
- Calculate adjusted point estimates and confidence intervals
- Some highlights:
- Automatic boundary recalculations during the trial for analysis with alpha spending approach, including under- and over-running
- Adaptive analysis tools for multi-arm trials
- Adaptive analysis tools for enrichment designs
Simulation Tool 🧪
Obtain operating characteristics of different designs:
- Assessment of adaptive sample size recalculation strategies
- Assessment of treatment selection strategies in multi-arm trials
- Assessment of population selection strategies in enrichment designs
Package Validation Concept ☑️
Why is rpact a reliable R package?
- Formal validation inspired by “GAMP 5” principles
- Validation documentation with > 8,000 pages
- As few dependencies as possible:
- Imports:
Rcpp - Suggests:
testthat,ggplot2,R6
- Imports:
- High test coverage:
rpact4.3.0 (Wassmer and Pahlke 2025): 39,128 unit tests (82% test coverage)
testPackage(): installation qualification on a client computer or the Roche servers (because of SLA in place)- We assume that base/core R is validated/reliable (see R-FDA.pdf)
RPACT Connect 🔗
- All important information and resources about RPACT on one dashboard page
- Roche-specific resources, e.g.,
- training slides,
- annual meeting slides, and
- the rpact validation documentation
- Use RPACT Connect to jump to RPACT Cloud and unlock advanced features
- Sign up: Please use your Roche email address so RPACT Connect can recognize your SLA membership automatically
- RPACT Connect: connect.rpact.com
Professional Support: SLA 🤝
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) with RPACT
- Be part of the “RPACT User Group”
\(\rightarrow\) yearly customer meetings - Get technical software support for written support requests
- Get company specific training
- Get company specific software validation documentation for each
rpactrelease on CRAN
- Get access to the members area at connect.rpact.com
- Make an
rpactinstallation qualification on Roche company servers / containers with your personaltestPackage()token and secret - Determine the direction of
rpactfuture development activities - Optional support for health authority interactions
- Optional consultation to support specific clinical trials
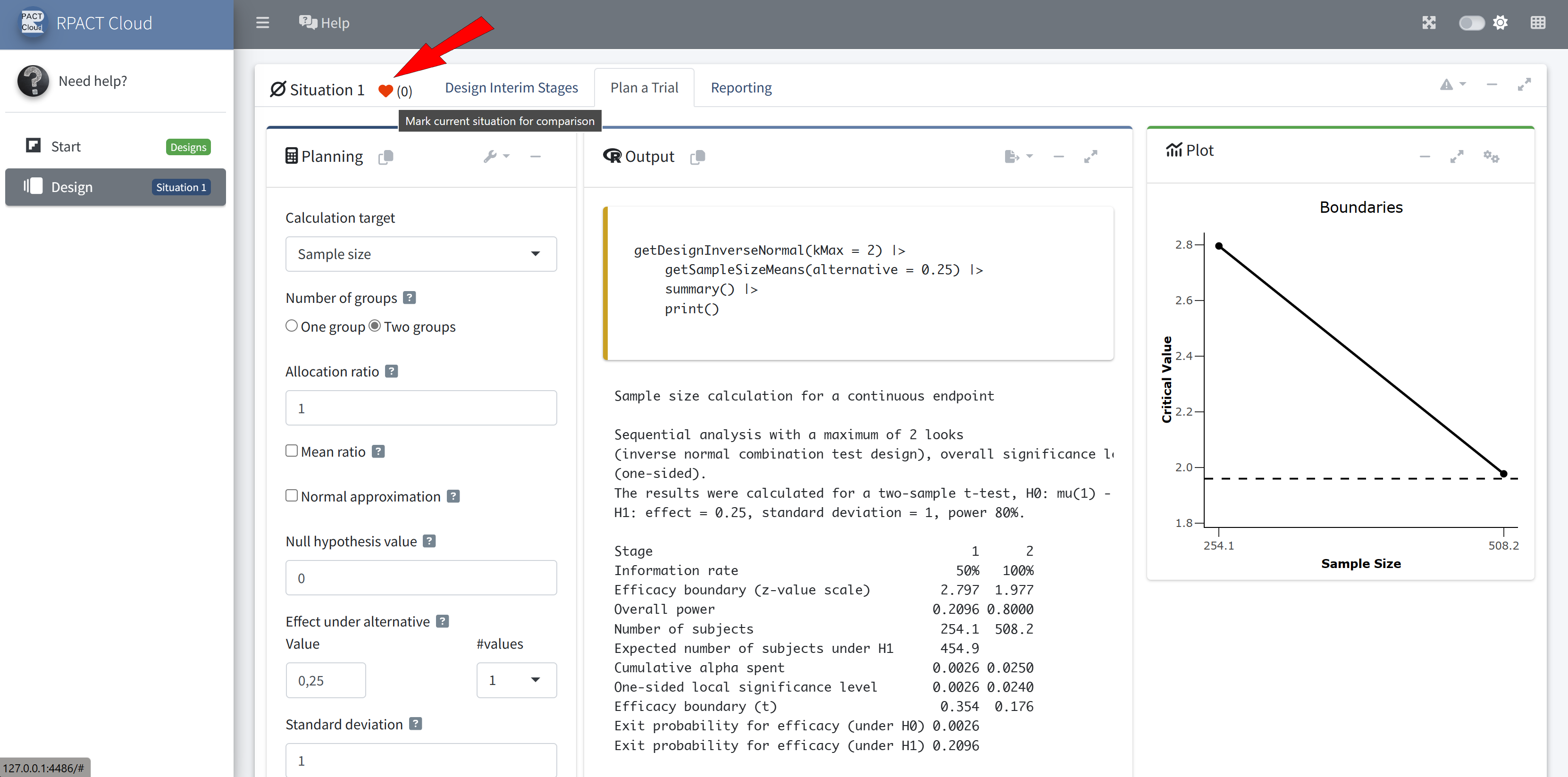
RPACT Cloud
RPACT Cloud ☁️
- Graphical user interface
- Web based usage without local installation on nearly any device ☁️
- Provides an easy entry to
rpact - Starting point for your R Markdown or Quarto reports
- Helpful to learn/demonstrate the usage of
rpactin a user friendly and intuitive way - Online available at rpact.cloud [free demo version]
Start Page
Design
Reporting

Design Comparison
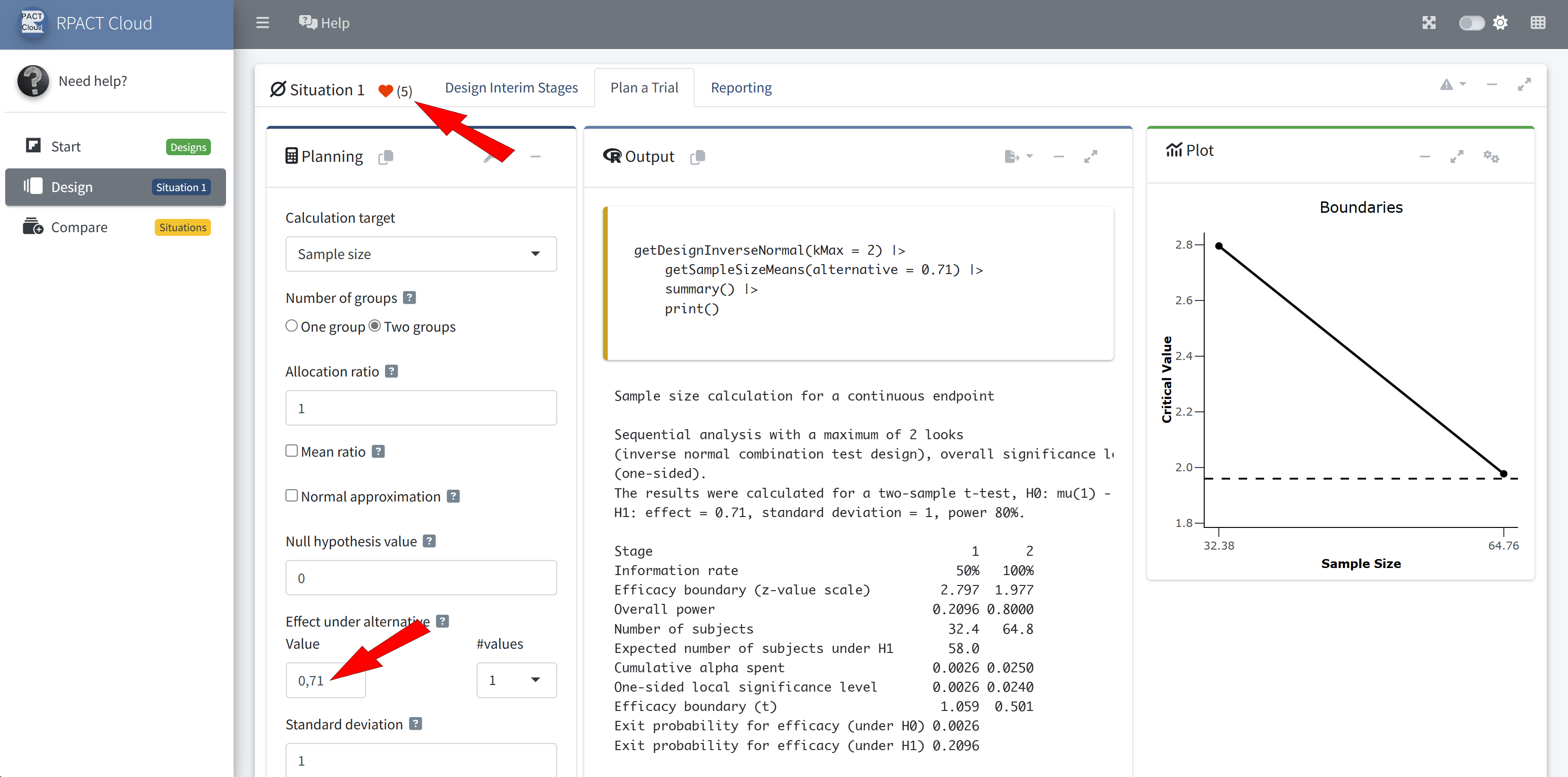
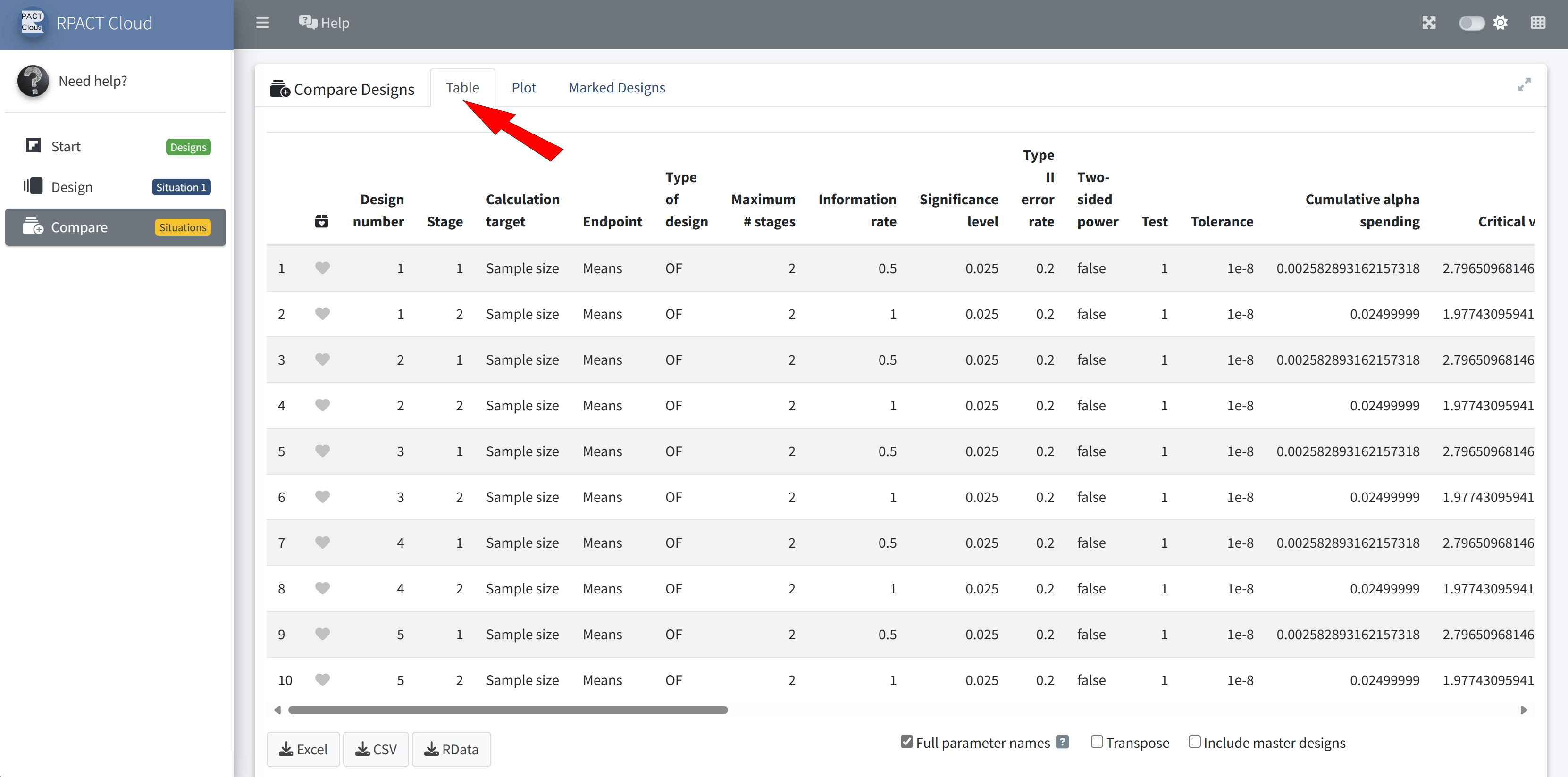
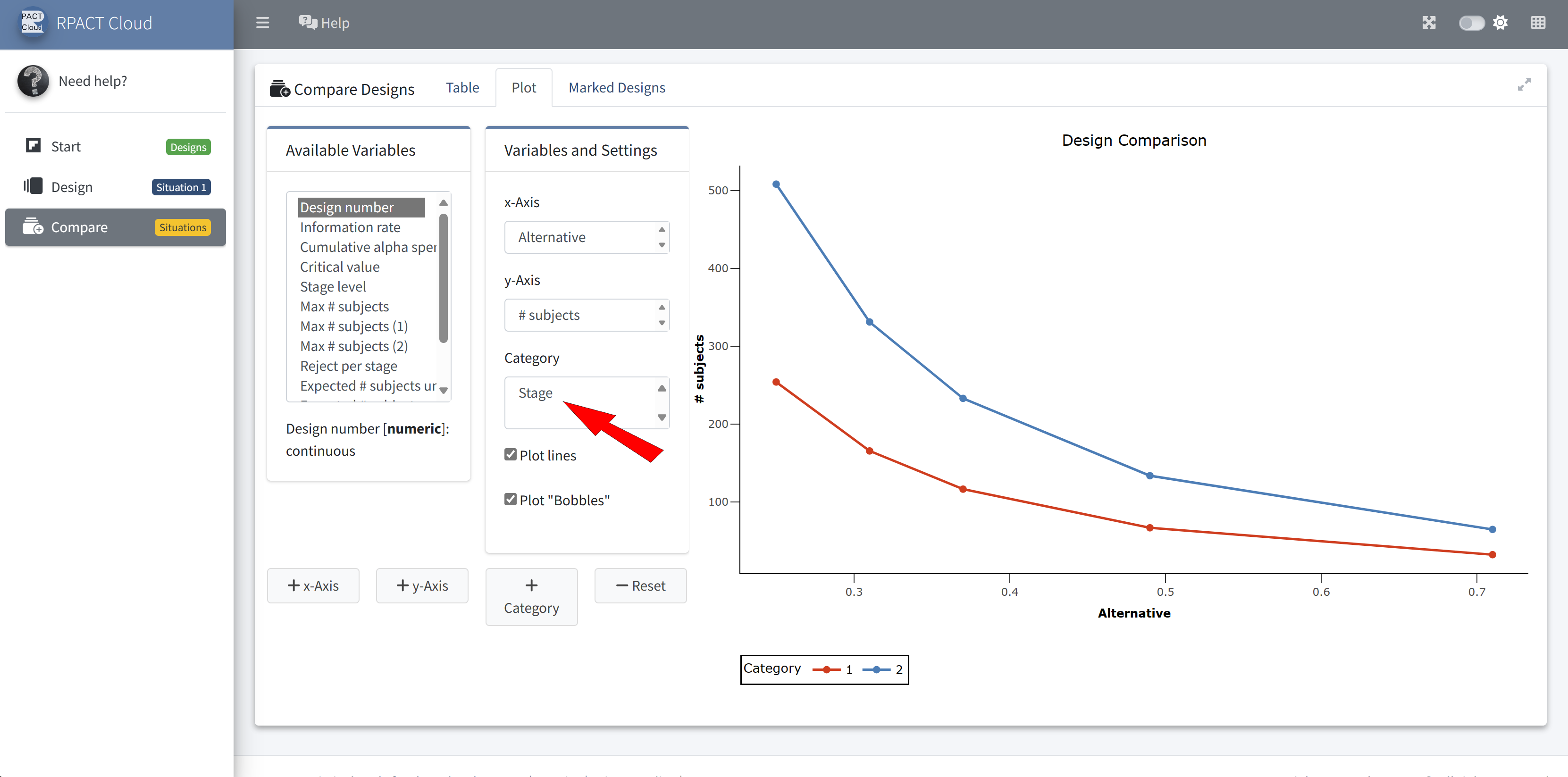
RPACT Cloud – Enterprise Licensing
Over the past year, four major pharmaceutical companies have licensed RPACT Cloud for internal installation and use on their own servers - fully replacing previous proprietary software.
To support these enterprise deployments, we published extensive documentation covering setup on Posit Connect, configuration, and full qualification/validation:
- How to Programmatically Clone and Deploy the RPACT Cloud Shiny App to Posit Connect
- Deployment: RPACT Cloud with RStudio Workbench to Posit Connect
- Installation: Running RPACT Cloud as an R Package
- Guide to Environment Variables for RPACT Cloud
- RPACT Cloud User Requirements Specification (URS)
- RPACT Cloud Test Report: The Test Report maps directly to the URS and documents the results of numerous shinytest2 unit tests, providing full transparency on validation outcomes
crmPack
Overview 📦
- Specialized R package for dose escalation trials
- Initial CRAN release in 2016, publication by Sabanés Bové et al. (2019)
- Higher flexibility compared to other software, thanks to its modular design
- Easy extensibility and adoption of new designs
- Produces visual and numeric outputs for easy interpretation
- Facilitates simulations to assess the performance under various scenarios
Large group of contributors 🏢
- Clara Beck (Bayer)
- Oliver Boix (Bayer)
- Prerana Chandratre (Bayer)
- Robert Adams (Bayer)
- Dimitris Kontos (ClinBAY/Bayer)
- Jiawen Zhu (Genentech)
- Ziwei Liao (Genentech)
- Daniel Sabanés Bové (Roche/RCONIS)
- John Kirkpatrick (Roche/Astellas)
- Giuseppe Palermo (Roche)
- Guanya Peng (Roche)
- Doug Kelkhoff (Roche)
- Wojciech Wojciak (Roche)
- Marlene Schulte-Goebel (Merck)
- Burak Kuersad Guenhan (Merck)
- Wai Yin Yeung (University of Lancaster/Roche)
- Thomas Jaki (University of Lancaster/Cambridge/Regensburg)
Framework
crmPack provides a highly flexible framework for the design and analysis of dose escalation trials. This schematic illustrates the framework’s key components and their interactions:
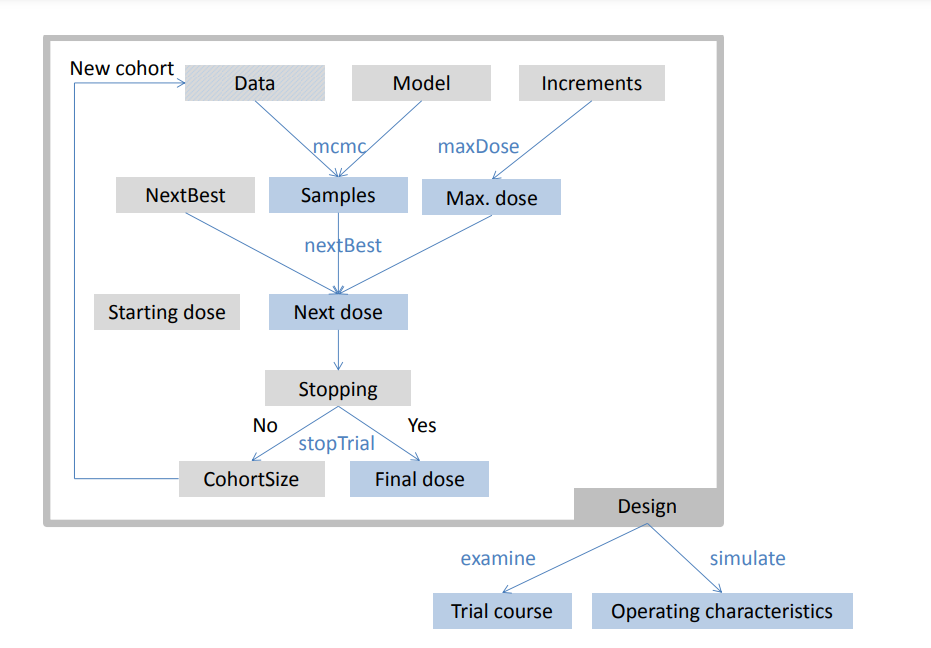
crmPack Framework
Example: Dose Escalation Design 💊
# remotes::install_github("openpharma/crmPack")
library(crmPack)
empty_data <- Data(doseGrid = c(1, 3, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 40, 50, 80, 100))
# Initialize the CRM model.
my_model <- LogisticLogNormal(
mean = c(-0.85, 1),
cov = matrix(c(1, -0.5, -0.5, 1), nrow = 2),
ref_dose = 56
)
# Choose the rule for selecting the next dose.
my_next_best <- NextBestNCRM(
target = c(0.2, 0.35),
overdose = c(0.35, 1),
max_overdose_prob = 0.25
)
# Choose the rule for the cohort-size.
my_size1 <- CohortSizeRange(
intervals = c(0, 30),
cohort_size = c(1, 3)
)
my_size2 <- CohortSizeDLT(
intervals = c(0, 1),
cohort_size = c(1, 3)
)
my_size <- maxSize(my_size1, my_size2)
# Choose the rule for stopping.
my_stopping1 <- StoppingMinCohorts(nCohorts = 3)
my_stopping2 <- StoppingTargetProb(
target = c(0.2, 0.35),
prob = 0.5
)
my_stopping3 <- StoppingMinPatients(nPatients = 20)
my_stopping <- (my_stopping1 & my_stopping2) | my_stopping3
# Choose the rule for dose increments.
my_increments <- IncrementsRelative(
intervals = c(0, 20),
increments = c(1, 0.33)
)
# Initialize the design.
design <- Design(
model = my_model,
nextBest = my_next_best,
stopping = my_stopping,
increments = my_increments,
cohort_size = my_size,
data = empty_data,
startingDose = 3
)Current Status
In December 2025, crmPack version 2.0 was released on CRAN (Sabanés Bové et al. 2025), which includes a ton of new features and improvements:
- Model-based designs (CRM), rule-based designs (3+3)
- Binary, time-to-event, dual efficacy/safety, ordinal outcomes
- 15 different models
- 14 different recommendation options
- 19 different stopping rules
- 9 cohort size rules
- 9 increment rules
- Reporting functionality (using
knitr) - 9 vignettes (documentation)
Professional Support: SLA 🤝
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) with RPACT
- Get technical software support for written support requests
- Get company specific training
- Get company specific software validation documentation for each
crmPackrelease on CRAN (coming in 2026)
- Make a
crmPackinstallation qualification on each Roche computer (coming in 2026) - Determine the direction of
crmPackfuture development activities (many new features coming in 2026!) - Optional support for health authority interactions
- Optional consultation to support specific clinical trials
Executive summary 📝
- RPACT company has been collaborating closely with Roche since its inception in 2017
- We presented two open source R packages for clinical trial design:
rpactfor confirmatory clinical trial designscrmPackfor dose escalation trial designs
- For both R packages, Roche has a Service Level Agreement (SLA) with RPACT for professional support, training, validation and development
- In total, 21 companies are currently having SLA with RPACT (21 for
rpact, 4 forcrmPack)
- In total, 21 companies are currently having SLA with RPACT (21 for
- In addition, we present briefly RPACT Cloud, a new web-based GUI for
rpact, which is currently licensed by 4 pharmaceutical companies

